India is a patchwork of art and craft forms. The Indian styles of paintings have unique origins and history behind them which make them even more interesting. This exhaustive list of different types of Indian paintings shows how every part of India added to its rich cultural heritage.
Andhra Pradesh - Kalamkari
Kalamkari means, “pen-art”. Kalamkari paintings are either hand painted or block printed on cotton fabric. This art form flourished under the rule of the Golconda Sultanat. It was first developed and evolved at Machilipatnam in Andhra Pradesh but its popularity soon spread to the other states. As far as the popular belief goes, in olden days, groups of artisans, musicians and singers known as chitrakattis would travel from village to village and narrate tales of Hindu mythology. As time passed, they even started illustrating these stories on canvas and thus Kalamkari was born.
Arunachal Pradesh - Thangka
A thangka, also known as tangka, thanka or tanka is a painting on cloth. The literal translation of the Tibetan word THANG KA means ‘recorded message’. Among all the art and crafts in Tawang, painting occupies a very special position. Not only it is essential for designing, decorating and finishing many mundane objects, but it is also a highly developed and important means of religious expression. It is a medium through which the Buddhist philosophy can be explained. Thanka paintings have a powerful and forceful impact on most people when they first encounter it.
Assam - Assamese Scroll Painting
Manuscript painting in Assam is part of a rich cultural heritage of Assam and India. It grew during the medieval period through the institution of satras. It was influenced by many painting forms and was used to preserve and spread knowledge through the satras and also in the wider society.
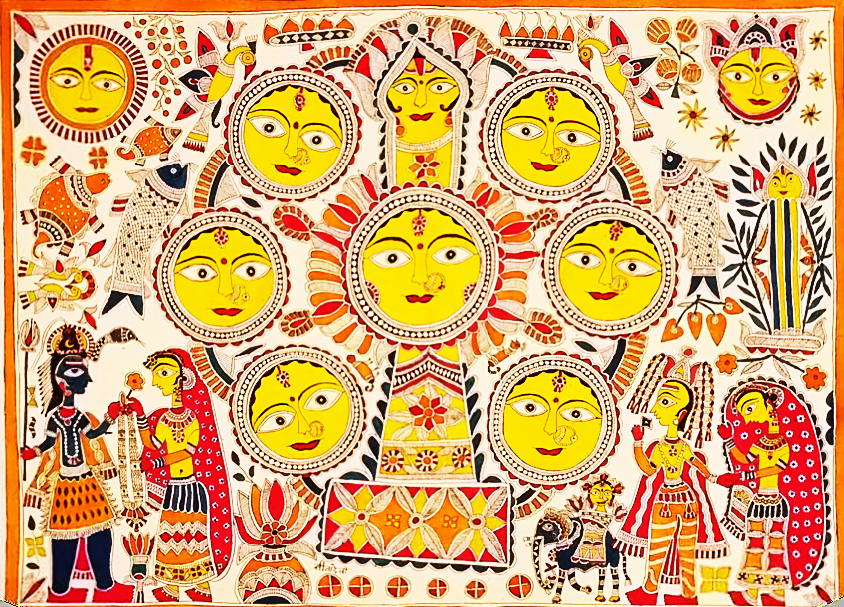
Bihar - Madhubani
These paintings find their origins and derive their name from a village called ‘Madhubani’ in Bihar. These paintings were first painted by the artists hailing from this village. King Janakraj, father of Sita wanted the artists to capture moments of Sita’s wedding ceremony with Lord Ram. Hence, these paintings came to be known as ‘Mithila’ Paintings. Predominately, the themes revolve around mythology, Hindu Gods and various royal court scenarios.
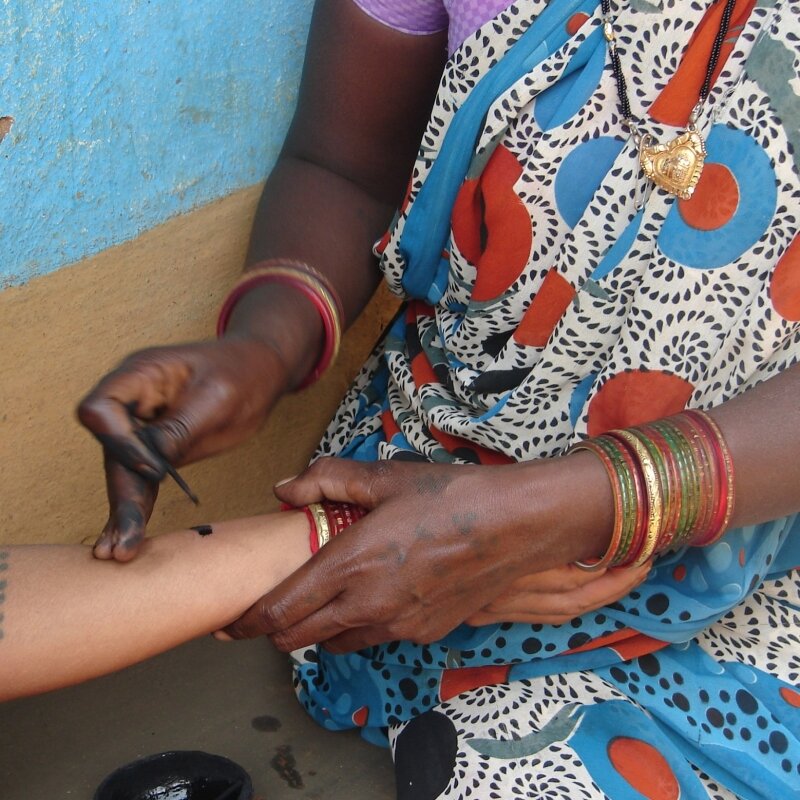
Chhattisgarh - Godna
The practice of tattooing is widely prevalent across Chhattisgarh. It is a form of body art practiced mostly by women on women, mainly amongst adivasi and 'lower' caste communities from this region. The word used for this practice is godna, which refers to the piercing of the body with needles
Goa - Folk Painting
The local handicrafts of Goa truly make for colourful souvenirs. From intricate wood carving to colourful wooden lacquerware, from sturdy bamboo craft to delicate papier-mâché, from fabulous terracotta and brassware to art pieces made from exotic sea shells, from intricate crochet and embroidery to rustic jute macramé, from delicate fibre craft to unconventional coconut masks, Goa’s art forms are as varied and colourful as the land itself.
Gujarat - Pithora Painting
Pithora paintings are highly enriched folk art culture of Gujarat done on the walls by several tribes such as the Rathwas and Bhilalas who live in the central Gujarat, 90 km (56 mi) from Vadodara, in a village called Tejgadh. Pithora paintings are more of a ritual than an art form.
Haryana - Sculpture
Sculpture, an artistic form in which hard or plastic materials are worked into three-dimensional art objects are famous in Haryana.
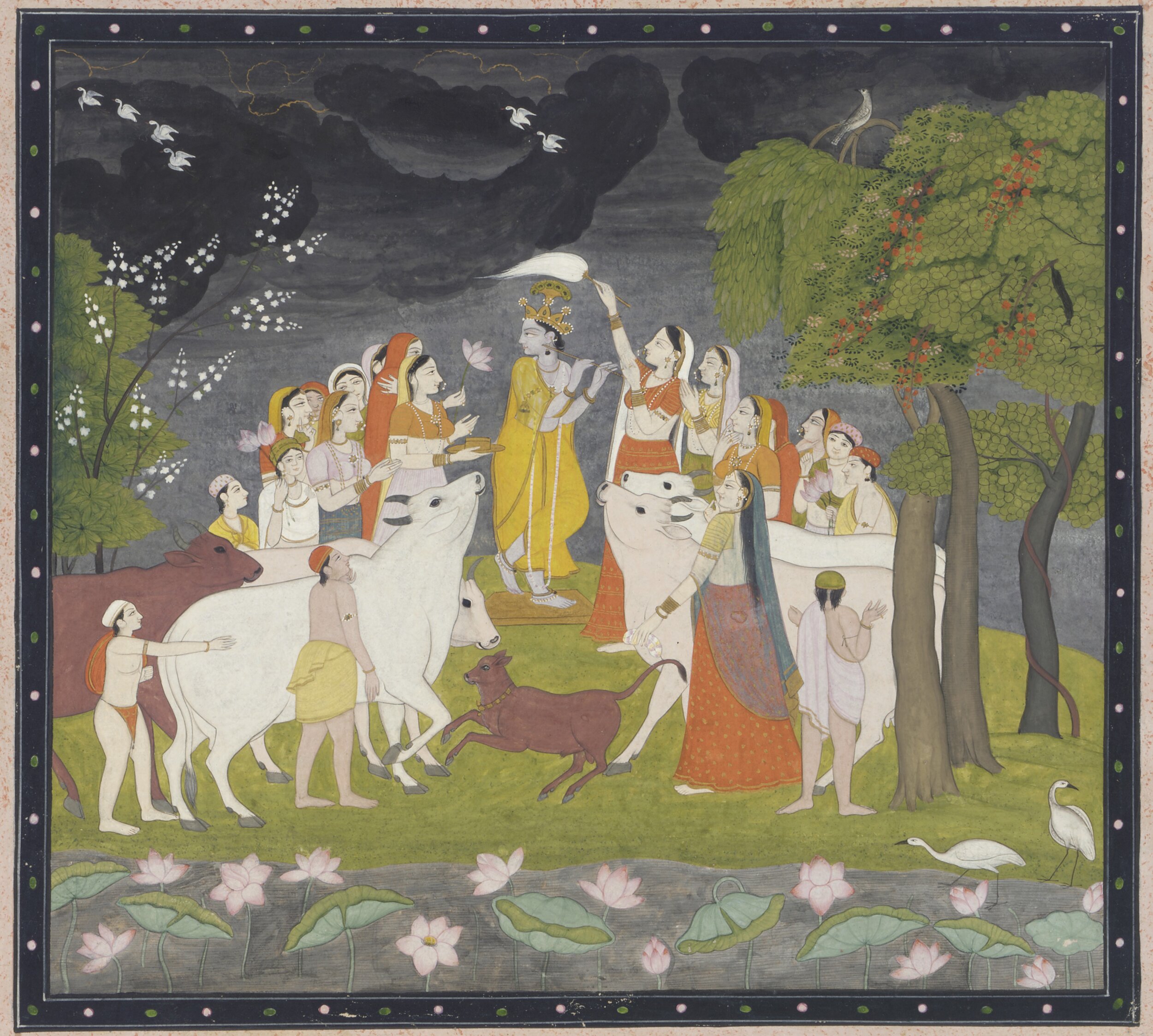
Himachal Pradesh - Kangra Painting
Kangra painting is the pictorial art of Kangra, named after Kangra, Himachal Pradesh, a former princely state, which patronized the art. It became prevalent with the fading of Basohli school of painting in mid-18th century, and soon produced such a magnitude in paintings both in content as well as volume, that the Pahari painting school, came to be known as Kangra paintings.
Jammu and Kashmir - Basholi
Basholi painting is a reputed school of miniature paintings known for its vivid, evocative colors, bold lines, and deep-set facial patterns. This style of painting saw its best years in the 17-18th century. Basholi (Basoli) is a town in Kathua district in the state of Jammu and Kashmir, India.
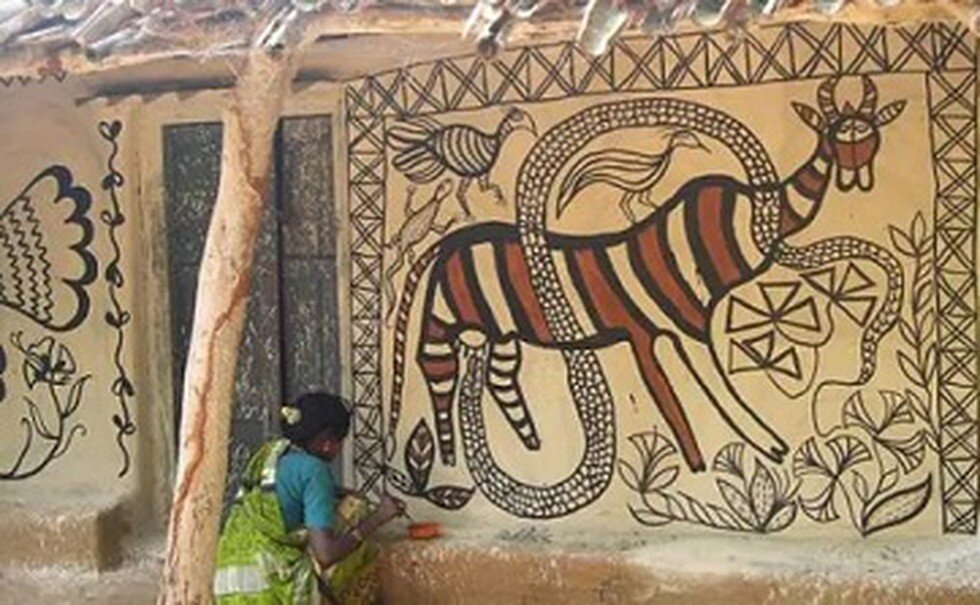
Jharkhand - Sohrai and Khovar Painting
Sohrai art is now known as the state art of Jharkhand. Railway stations in the towns like Hazaribagh and Jamshedpur now greet travellers with Khovar and Sohrai murals that only adorned village homes until recently. Sohrai paintings are age-old tribal traditional paintings based on nature themes – forest, people and animals etc. The paintings are done by tribal women using natural ingredients such as different shades of clay and charcoal.
Karnataka - Chittara
Chittaras are intricate wall paintings traditionally created by the tribal women of Malnad on their red mud-coated houses, as well as rangoli floor designs. The traditional paddy husk kalash can be found painted with chittara art, as can papier mache and terracotta vases.
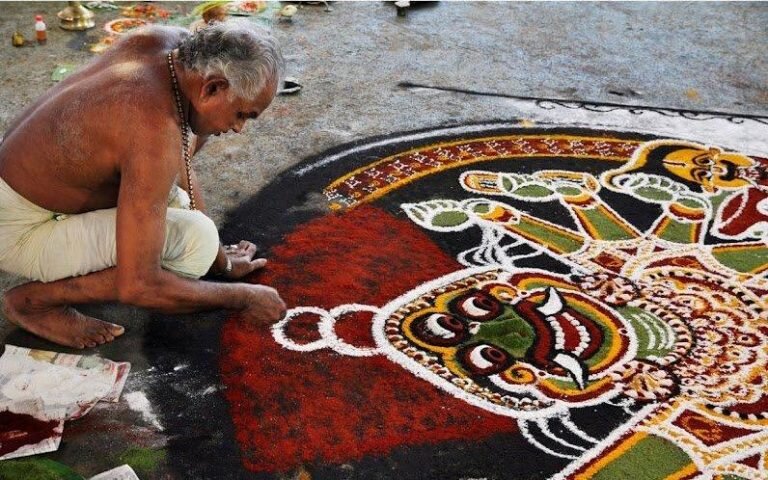
Kerala - Kalamezhutgu
Kalamezhuthu is an ancient art woven into the ritualistic mores of Bhagavati, Naga and Ayyappa temples in Kerala. It refers to the pictorial representation of deities on the floor (kalam) using coloured powders (kolappodi) during ceremonies.
Ladakh - Thangka Painting and Mural
Religious Art, Early 20th century, From the collection of: Dastkari Haat Samiti. The culmination of Tibetan Buddhist art, thangkas are pictorial religious scrolls. Most often hand painted with mineral colours and gold dust, traditional thangkas were also embroidered or appliqued.
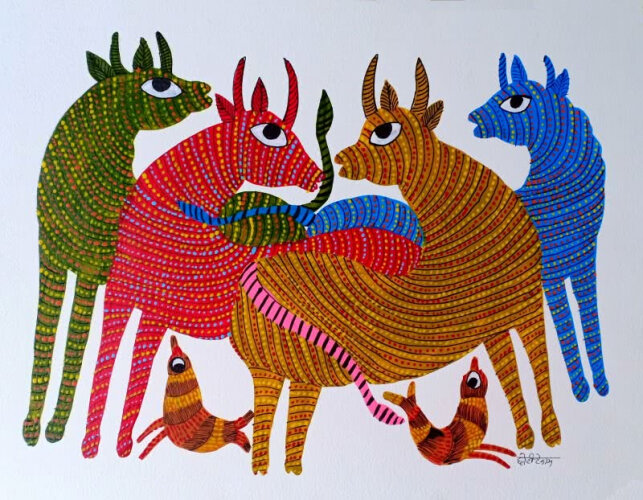
Madhya Pradesh - Gond
Characterised by a sense of belonging with nature, the Gondi tribe in Madhya Pradesh created these bold, vibrantly coloured paintings, depicting mainly flora and fauna. The colours come from charcoal, cow dung, leaves and coloured soil. If you look closely, it is made up of dots and lines. Today, these styles are imitated, but with acrylic paints. It can be called an evolution in the Gond art form, spearheaded by Jangarh Singh Shyam, the most popular Gond artist who revived the art for the world in the 1960’s.
Maharashtra - Warli Painting
Warli art is a 400-year-old tribal art form from Maharashtra. Painted mostly by the Warli tribe women, paintings in this art form are based on nature, harvest, weddings and fertility. Initially painted on the walls of the houses, Warli Art has gained immense popularity and is painted on home furnishings, décor, and murals.
Manipur - Block Painting
It is one of the oldest and most enjoyable of all the crafts and has given color and pattern to paper, cloth, and other surfaces for nearly 4,000 years. Today the process is essentially the same and very well known in Manipur.
Meghalaya - Wood Carving
The state of Meghalaya is well known for various crafts. Handicrafts made with cane and bamboo products, textile weaving, carpet weaving, ornament making and woodcarving also hold important place in Meghalaya's art and crafts. In fact, weaving forms an integral part in the culture of the state and its tribes. Wood carving of Meghalaya is an ancient art that flourished in the rural parts of Meghalaya, especially around the Garo hills.
Mizoram - Textile Painting
The textiles of Mizoram constitute one of the most significant art and crafts of the region. The textile industry of Mizoram offers a variety of garments, which are quite popular in the north-western part of the country of India. Many Mizo people are well known as skilled weavers. Weaving is one of the most important segments of the cultural life of the people of this state. The women are involved in weaving in Mizoram from a very early age.
Nagaland - Cloth Painting
Cloth painting is a very popular form of painting of Nagaland. The natives belonging to the Lotha, Ao and Rengma tribal communities practice this highly skilled art of painting on clothes. The art of painting is quite similar to that of the Rengmas even though the basic pattern is quite different.
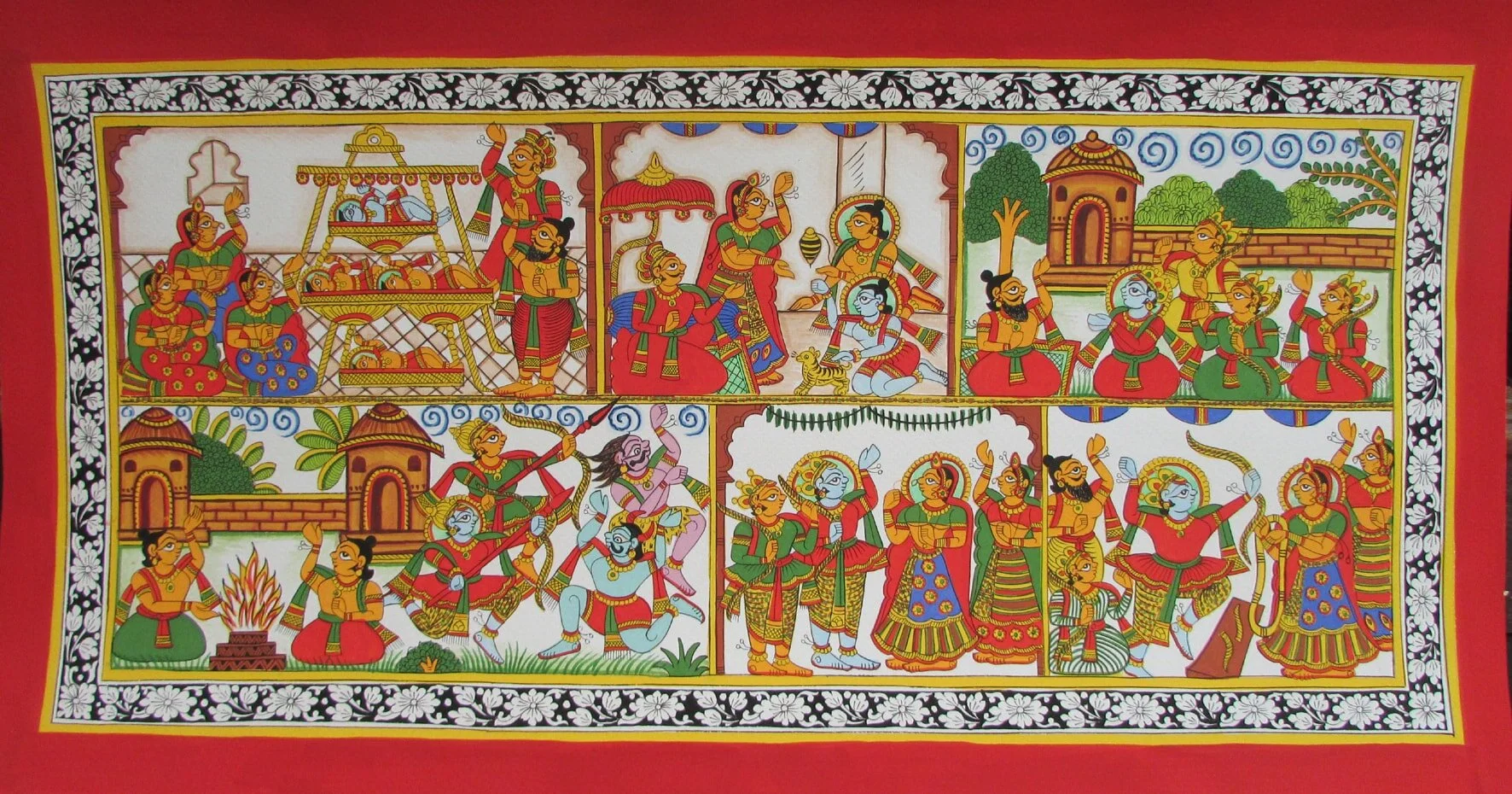
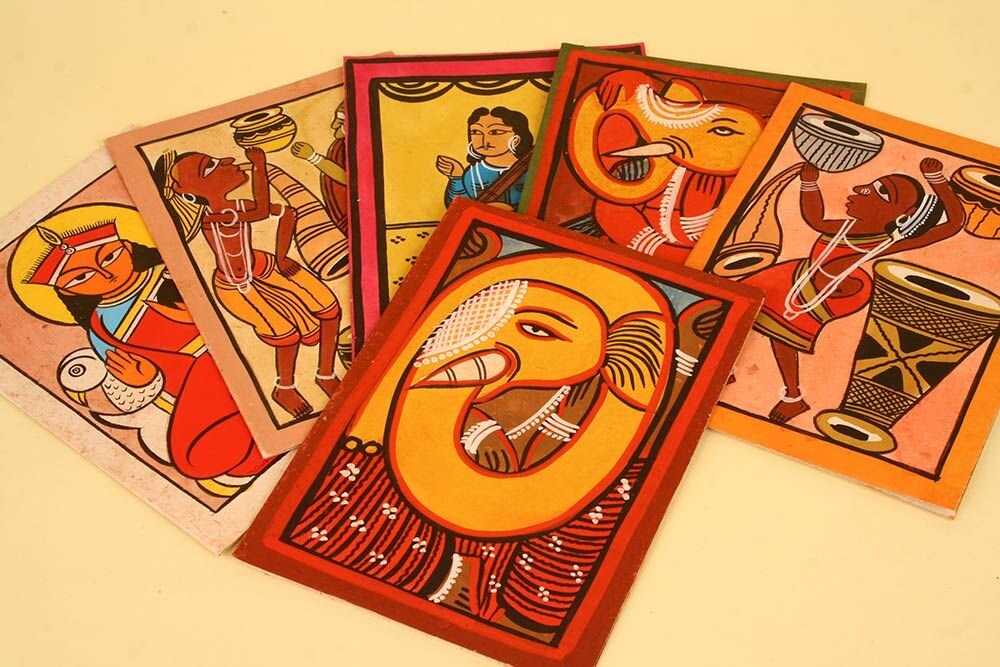
Odisha - Pattachitra
Pattachitra folk painting hails from the state of Orissa. They originated during the 8th century and is suppose to be one of the earliest forms of indigenous art. ‘Patta’ means ‘clothing’ and ‘chitra’ stands for paintings, so pictures in this art form are painted on a cloth base. Pattachitra art is inspired by the Jagannath and Vaishnava culture. Depictions of Pattachitra art can be seen in the famous Konark Temple in Orissa.
Punjab - Mud-Work
Mud works is one of the earliest art forms of Punjab that gained popularity. Mud work in Punjab started as a result of some superstitions to keep away evil spirits. Slowly, designing of different motifs gave rise to a new art expression. Done mainly by rural women, it is practiced generally during many festivals like Navaratri, karva-Chauth, Holi and Diwali.
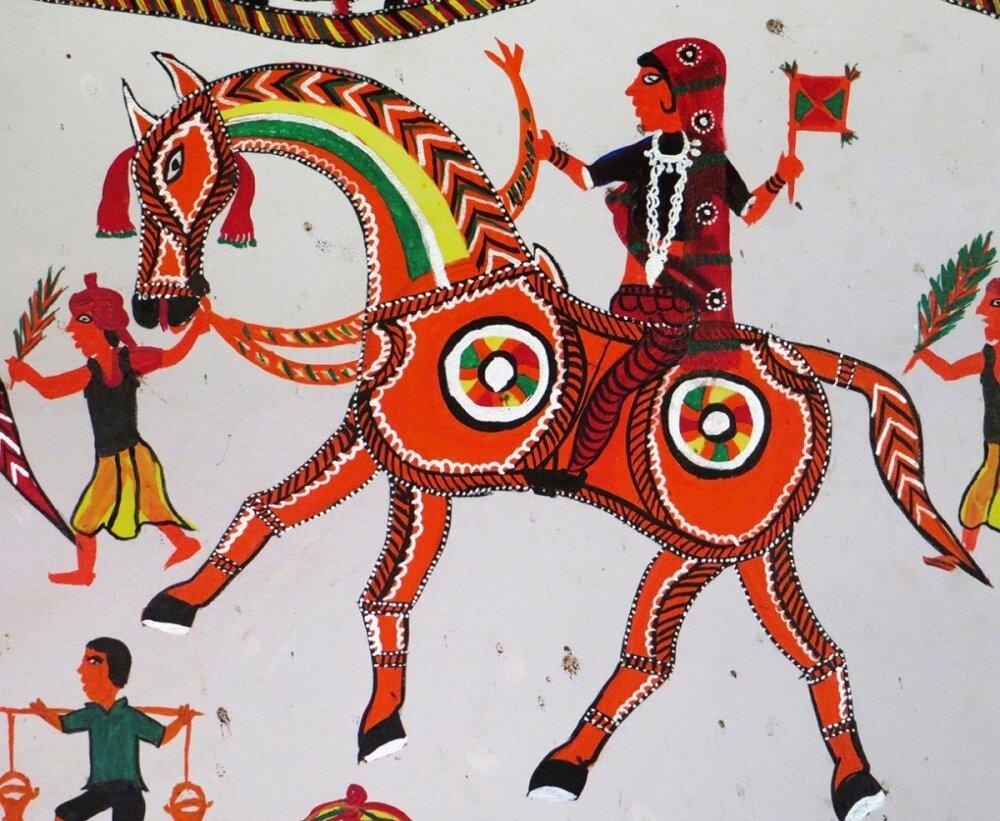
Rajasthan - Phad Painting
Originating in Rajasthan, Phad is mainly a religious form of scroll painting depicting folk deities Pabuji or Devnarayan. The 30 or 15 feet-long canvas or cloth that it is painted on is called phad. Vegetable colours and a running narrative of the lives and heroic deeds of deities characterise these paintings.
Sikkim - Thangka
A thangka, variously spelt as thangka, tangka, thanka, or tanka is a Tibetan Buddhist painting on cotton, silk appliqué, usually depicting a Buddhist deity, scene, or mandala. Thangkas are traditionally kept unframed and rolled up when not on display, mounted on a textile backing somewhat in the style of Chinese scroll paintings, with a further silk cover on the front. So treated, thangkas can last a long time, but because of their delicate nature, they have to be kept in dry places where moisture will not affect the quality of the silk.
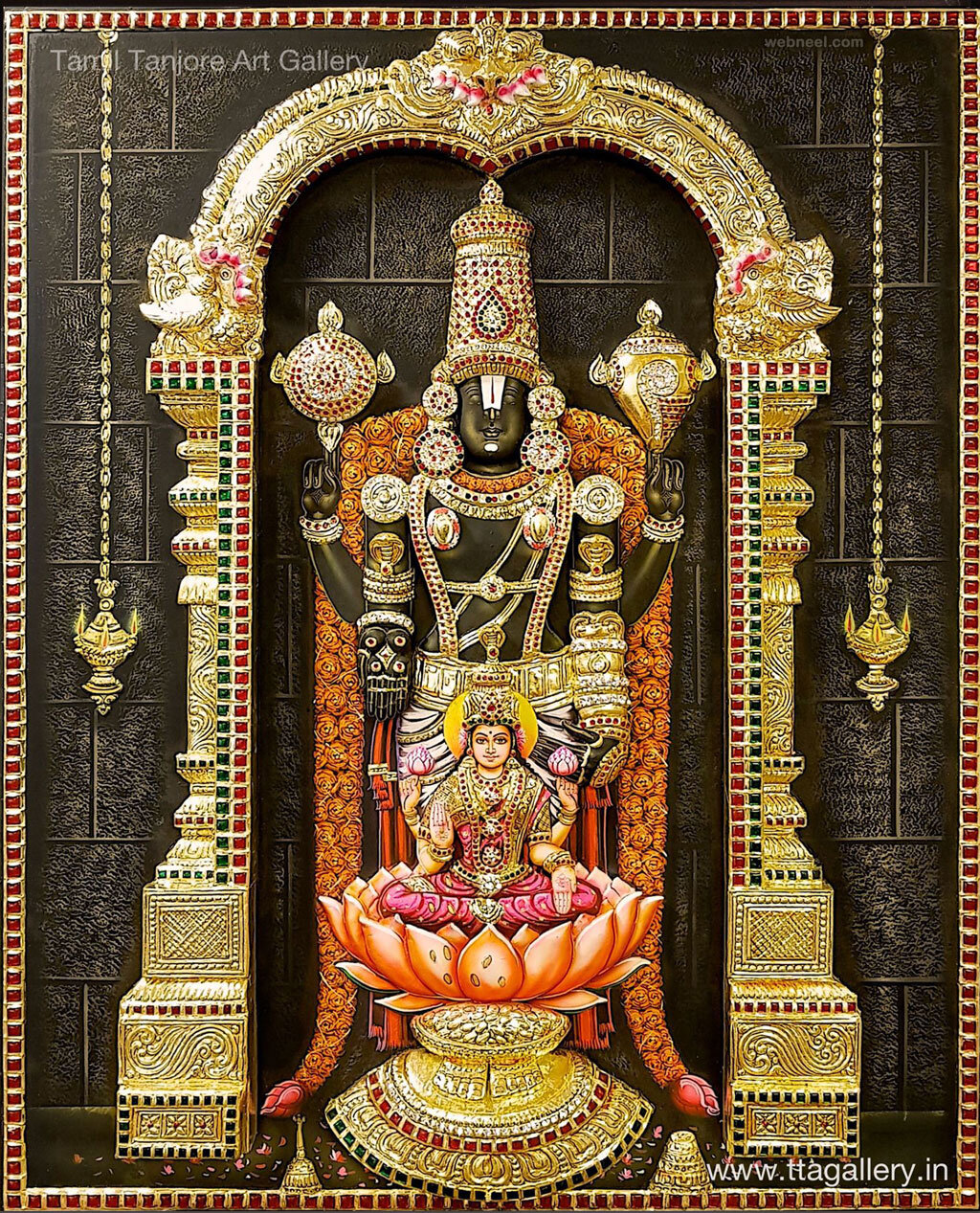
Tamil Nadu - Tanjore
Tanjore style of paintings were first painted during the 16th century and under the Chola regime, this art form found its calling. Known for its use of vibrant colours, rich surfaces, and embellishments, Tanjore paintings originated from the Thanjavur district in Tamil Nadu. The themes of Tanjore paintings are mostly Hindu Gods and Goddesses. Interestingly, the main subject is always painted in the center of the frame. Tanjore Paintings are painted on wooden planks which are colloquially known as ‘Palagai Padam‘.
Telangana - Cheriyal Scroll Painting
Originating in Telangana, this dying art form is practised by the Nakashi family only, where it has been passed down for many generations. The tradition of long scrolls and Kalamkari art influenced the Cheriyal scrolls, a much more stylised version of Nakashi art. Depicting puranas and epics, these 40-45 feet scrolls were an essential visual accompaniment as saints wandered around singing or narrating the epics. They resemble modern-day comic panels, with about 50 on each scroll. They use primary colours and a vivid imagination, a stark contrast from the traditional rigour of Tanjore or Mysore paintings.
Tripura - Bamboo Work
Cane & Bamboo Handicrafts of Tripura – among the best in the country. 60% of the requirement of the entire country for bamboo sticks for Agarbatti-making is met from the State. Tripura Bamboo Mission (TBM) has been launched in 2007, under PPP framework, for integrated development of Bamboo Sector.
Uttar Pradesh - Sanjhi
Sanjhi Painting is a tradition of art that originated out of the cult of Krishna and flourished in the north Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is in Vraja, or Vrindavan, the homeland of Lord Sri Krishna, that this art of Sanjhi painting reached its pinnacle. This art painting is rooted in the folk culture of the region. It was taken to its glory by the Vaishnava temples in the 15 th and 16 th century. Sanjhi came to be regarded as a highly refined art form practiced by the Brahmin priests.
Uttarakhand - Aipan
Aipan is a ritualistic folk art, native to the Kumaon region of Uttarakhand. It is drawn to commemorate auspicious occasions, festivals and even rituals performed during death of a person. The art form is also known to offer protection against evil.
West Bengal - Kalighat Painting
Originated in the 19th century Bengal, from Kalighat. It was the time when upheaval against the British was a possible, exciting idea. These paintings, on cloth and pattas, at first depicted Gods and Goddesses, but then took a turn towards social reform. With cheap paper and paint colours, squirrel hair brushes and colour pigments, the art was characterised by flawless strokes, brushwork, and simple but bold drawings. It sought to raise awareness about social conditions in its viewers – rich zamindars were depicted drinking wine with women, while priests were shown with ‘unchaste’ women and police babus being sloppy.